What is the secret to running profitable affiliate campaigns? If you are stepping into the world of performance‑based marketing, you need to speak the language. This Affiliate Marketing Glossary breaks down 50+ key terms from basics to advanced strategies that every affiliate must know. Mastering this vocabulary is the first step to running smarter campaigns, tracking results with confidence and boosting your earnings.

Use this glossary as a foundational guide to understanding affiliate marketing. This guide will cover Link Management and Marketing Terms that are essential for any successful affiliate in 2026.
Foundational Terms in Affiliate Marketing
Every successful affiliate campaign starts with a strong foundation. These core terms give you the clarity and confidence to navigate the basics of affiliate marketing.
1. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate Marketing is a type of performance-based marketing where a business rewards one or more affiliates for each visitor or customer brought by the affiliate’s own efforts. This means you earn a commission for promoting a product or service. This business model is built entirely on successful conversions tracked through specialized links.

Example: A blogger reviews a hosting service and earns a 10% commission when a reader buys that service through the special link provided in the review.
2. Affiliate
An affiliate is an individual or a company that promotes a merchant’s product or service in exchange for a commission. Affiliates are also often called publishers or partners. They act as a bridge between the customer and the merchant.
Example: You are an affiliate for a software company promoting their product on your blog and social media channels.
3. Merchant or Advertiser
The merchant or advertiser is the business or individual behind the product or service. They set up the affiliate program and handle commission payouts. Affiliate marketing is one of their key channels for increasing visibility and generating sales, complementing their broader marketing strategy.
Example: Amazon or HubSpot are merchants who run large affiliate programs for their products and services.
4. Affiliate Program
An affiliate program is the system set up by the merchant to manage all their affiliates, track sales and handle commission payouts. This program defines the rules, commission rates and payment schedule. Most programs use dedicated software to manage these operations.
Example: A software company offers a 30% recurring commission through its official affiliate program.
5. Commission
Commission is the monetary reward an affiliate receives for driving a successful conversion, which is usually a sale, a lead or a click. It can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the sale price. This is the core revenue stream in Affiliate Marketing.
Example: If the product costs $100 and the commission rate is 15% the affiliate earns $15 per sale.
6. Cookie Duration
Cookie duration is the length of time the merchant’s tracking software attributes a sale to the affiliate after the user clicks the Affiliate Link. If the user makes a purchase anytime within this period, the affiliate still earns the commission.

Example: A 30-day cookie means if a user clicks the link today and buys the product 25 days later, the affiliate gets credit.
7. Conversion
In Affiliate Marketing, a conversion is a desired action completed by the customer after clicking the Affiliate Link. This action can be a purchase, a form submission, a trial sign-up up or a download. The type of conversion determines the commission structure.

Example: For a software company, a conversion might be a completed free trial sign-up.
8. CPA (Cost Per Acquisition)
CPA means Cost Per Acquisition. It is a payment model where the affiliate earns a commission every time a specific action is completed such as a sale, a lead or a download. This is a common payment structure for many programs.
CPA = Advertising Spend / Acquisitions Generated
Example: The merchant pays the affiliate $50 every time a visitor signs up for a free demo after clicking their Affiliate Link.
9. EPC (Earnings Per Click)
Earnings Per Click is a metric used to calculate the average amount of money an affiliate earns every time a person clicks on one of their Affiliate Links. This metric is often calculated over a specific period, like 30 or 60 days. EPC helps affiliates compare the performance of different programs.
Example: If an affiliate makes $1000 from 1000 clicks, the EPC is $1.00.
10. Recurring Commission
Recurring Commission is a payment structure where the affiliate earns a commission not just on the initial sale but also on all subsequent subscription renewals or recurring payments made by the customer. This model is very popular with Software as a Service or SaaS products.

Example: An affiliate promotes a monthly subscription tool and earns 20% every month as long as the customer remains subscribed.
11. Super Affiliate
A super affiliate is an affiliate who drives a very high volume of traffic and sales for a merchant. They typically have a large established audience or a significant marketing budget. Super affiliates often receive higher commission rates or special deals.
Example: A popular YouTube personality with millions of subscribers who promotes products is considered a super affiliate.
12. Niche
A niche is a specialized segment of the market that the affiliate focuses on. Focusing on a niche allows the affiliate to become an authority in that specific area and attract a highly targeted audience. This specialization leads to higher conversion rates.
Example: Instead of promoting general fitness products, an affiliate focuses specifically on yoga equipment for seniors.
13. Affiliate Network
An affiliate network acts as an intermediary marketplace, connecting merchants (who host their programs) with affiliates (who look for products to promote). The network handles tracking, reporting, and payment processing for both parties. They simplify administration and provide a vast catalog of programs.
Example: Platforms like ShareASale, CJ Affiliate or ClickBank are large-scale affiliate networks where merchants list their products and thousands of affiliates find links to promote.
14. Flat Deal
A flat deal is a commission structure where the affiliate earns a fixed monetary amount for every conversion, regardless of the product’s price or the total order value. This is common for lead generation or low-cost products, where simplicity is preferred over percentage calculations.
Example: Promoting a $10 e-book with a 50% commission yields $5, while a flat deal might offer a fixed $5 commission for every successful download, even if the price changes later.
15. Payment Threshold
The payment threshold is the minimum amount of accumulated commission an affiliate must earn before the merchant or network will issue a payment. This prevents excessive fees and administrative costs associated with processing small, frequent payouts.
Example: If the payment threshold is set at $100, an affiliate with only $75 in commissions will have to wait for the next month’s earnings to surpass that $100 mark before receiving any money.
Link Management Terms and Best Practices
The links you use are the lifeline of your Affiliate Marketing business. Mastering their technical aspects is critical for both commission security and SEO. These Link Management Terms help you secure your earnings and improve your site’s health.
16. Affiliate Links
Affiliate Links are the unique tracking URLs provided by the merchant to the affiliate. Every click on an Affiliate Link is recorded to ensure the affiliate receives credit for the sale. These links contain a unique ID specific to the affiliate.
Example: ‘merchant.com/?affid=XYZ123&product=ABC‘ is a standard Affiliate Link.
17. Link Cloaking
Link cloaking is the process of replacing long, cluttered affiliate URLs with clean, branded links. This makes them look more professional and trustworthy to users, while also adding a layer of protection against commission theft. Plugins like BetterLinks make this process seamless, helping affiliates manage and present their links more effectively.

Example: Changing merchant.com/?affid=XYZ123 to yourdomain.com/go/productname.
18. Link Shortening
Link shortening is the process of making a long URL much shorter and more manageable. This is important for social media sharing and for creating easy-to-remember vanity URLs. This is often done in conjunction with link cloaking.
Example: A 100-character URL becomes yourdomain.com/go/offer.
19. Link Management
Link Management is the practice of organizing, tracking, optimizing and maintaining all the links on a website, especially Affiliate Links. This ensures all links are secure, working correctly and contributing positively to SEO. This is a vital task for any large-scale website.

Example: Imagine having a single dashboard where you can sort all your affiliate links, see which ones are performing best, fix broken URLs instantly and update link destinations with one click, rather than hunting through dozens of pages.
20. Link Building
Link Building in the context of SEO is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own. While typically external, it is important for affiliates to also master internal Link Building to boost the authority of their review and comparison pages.

Example: Writing a guest post for another blog and including a link back to your high-value product review page.
21. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink. For SEO purposes, the anchor text should be relevant and descriptive of the page it links to. Using targeted keywords in the anchor text helps improve the search ranking of the destination page.

Example: In this blog, whenever we add a hyperlink, the visible clickable words are called the anchor text. For instance, in the sentence ‘You can download the software here,’ the phrase ‘download the software’ serves as the anchor text.
22. Deep Linking
Deep linking involves linking directly to a specific product page or content page on the merchant’s website rather than just the homepage. This leads the user directly to the relevant content, which often results in higher conversion rates.
Example: Linking directly to the product’s checkout page instead of the general category page.
23. Link Redirection (301, 302, 307)
A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested. A 301 is a permanent redirect, while a 302 is temporary. Correctly managing redirects is essential for maintaining SEO value.

Example: If a product is out of stock, you use a 302 redirect to temporarily send traffic to a similar product page.
BetterLinks allows for easy creation and management of all link redirects, ensuring no traffic is lost due to old or broken Affiliate Links.
24. Link Rot
Link rot is a term for the natural decay of hyperlinks over time, where links become broken or irrelevant. Broken Affiliate Links result in lost commissions and a poor user experience. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent link rot.
Example: A merchant discontinues a product and the Affiliate Link leads to a 404 error page.
BetterLinks includes a broken link check feature to help affiliates quickly identify and fix any broken Affiliate Links, preventing lost revenue.
25. Link Expiration
Link expiration is a feature that allows an affiliate to set a specific date or time when an Affiliate Link will automatically redirect to a new URL. This is useful for time-limited offers or promotions.

Example: A holiday sale link automatically redirects to the merchant’s homepage after December 31st.
BetterLinks offers a link scheduling and expiration feature, ensuring promotional Affiliate Links never lead to outdated or frustrating offers.
26. Click Limit
A click limit is a control feature where an affiliate can set a maximum number of clicks an Affiliate Link can receive before it automatically redirects to a different URL. This is often used for exclusivity deals or budget control.
Example: An affiliate can set a limit of 100 clicks on a special offer link, ensuring only the first 100 users get the deal.
27. Dynamic Redirects
Dynamic redirects or conditional redirects allow the affiliate to send traffic to different destination URLs based on specific conditions like the user’s location, device, or time of day. This is key for A/B testing and localized offers.

Example: A user from the US is sent to the US landing page while a user from the UK is sent to the UK landing page for the same product.
Tracking And Optimization Terms
Success in Affiliate Marketing is measured by data. These Terms relate to how you monitor traffic, analyze conversions and optimize your entire Marketing strategy for better SEO.
28. Tracking
Tracking is the process of monitoring user activity after they click an Affiliate Link, including clicks, conversions and sales. Accurate tracking is the foundation of the entire business model as it ensures the affiliate gets paid.
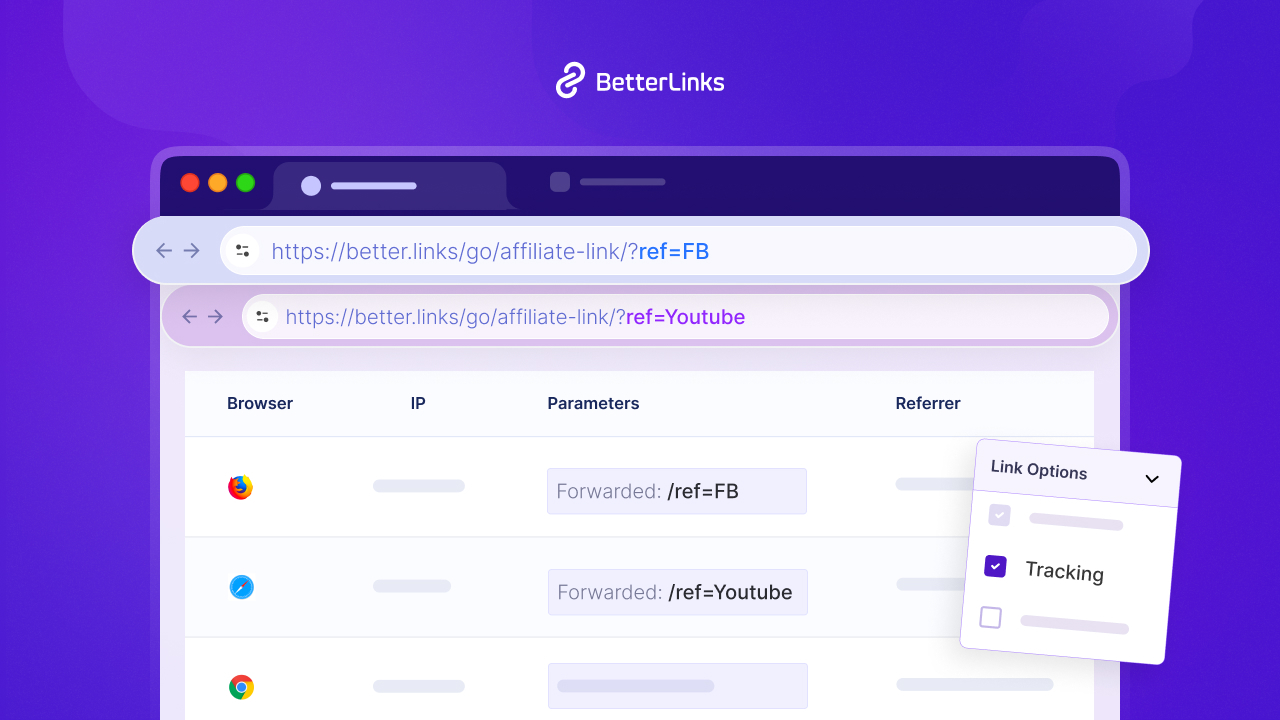
Example: The merchant’s system records a click when a user goes to their site and then records a sale when that user completes a purchase.
BetterLinks provides detailed built-in analytics for robust link tracking, including geographic data and browser statistics.
29. UTM Parameters
UTM Parameters are small codes added to a URL to track where visitors come from and which marketing efforts drive clicks. The source shows where the traffic originated, the medium explains how it arrived, the campaign identifies the specific promotion and the term highlights the keyword used in paid ads.
- Source: Source identifies where the traffic originated (e.g., Facebook, Google, newsletter).
- Medium: Medium specifies how the traffic arrived (e.g., email, social, CPC, referral).
- Campaign: Campaign tracks the specific promotion or initiative driving the click (e.g., Summer Sale, BFCM2026).
- Term: Term highlights the keyword or targeting detail used in paid campaigns (e.g., “best running shoes”).
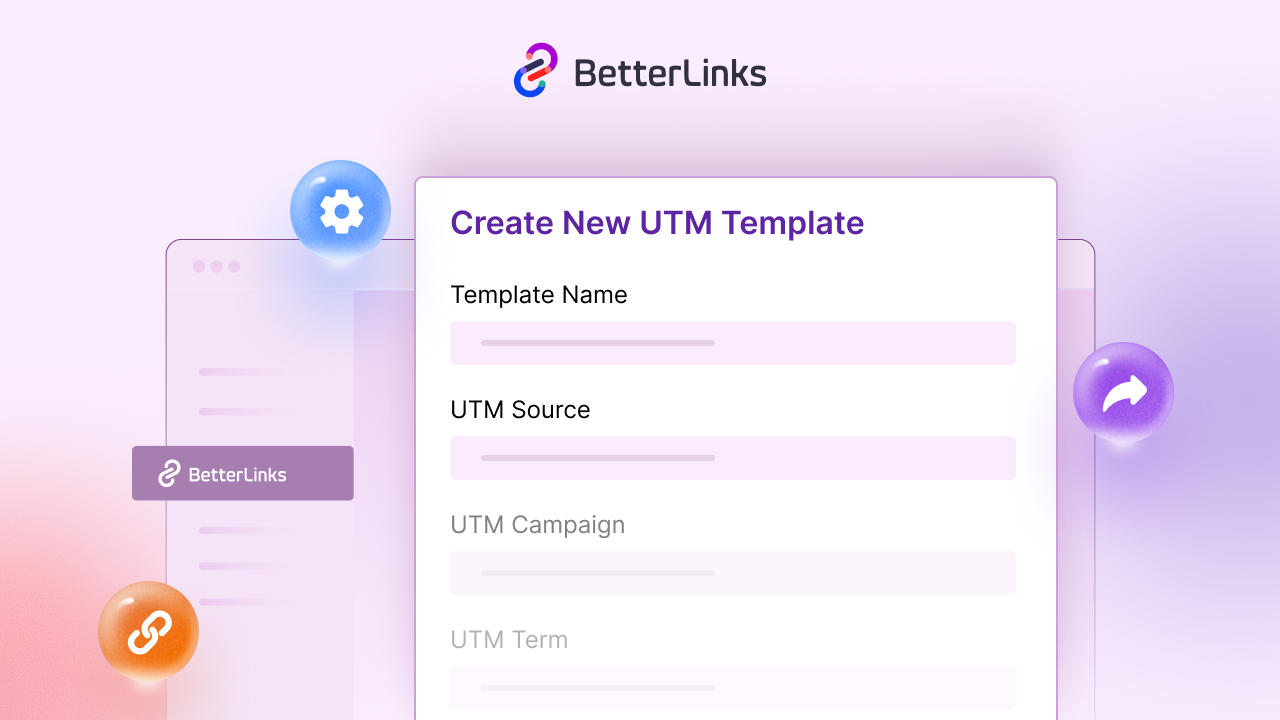
Example: ?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=post&utm_campaign=summer_sale.
BetterLinks features an integrated UTM Builder allowing affiliates to easily create and manage these tracking tags for every link.
30. Real Time Reporting
Real-time reporting refers to the ability to see data on link clicks and user activity as it happens. This allows affiliates to make quick decisions for campaigns that are performing well or badly.
Example: Watching the number of clicks on a new social media post increase in the analytics dashboard right after posting.
31. SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results. For affiliates, good SEO means getting their review posts and comparison articles to rank highly in Google.

Example: Optimizing a blog post about the ‘best email marketing tool’ so it ranks on the first page of Google.
32. Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the visitors that come to your website from unpaid listings on search engine results pages like Google or Bing. This is highly valued traffic because it is free and often highly motivated. It is a direct result of effective SEO.

Example: A user searches for ‘best running shoes’ and clicks on your well‑optimized product review that appears on the first page of search results, above the fold and among sponsored listings. The traffic you receive from that click is Organic Traffic.
33. Conversion Rate
Conversion Rate is the percentage of visitors who complete a desired goal or conversion out of the total number of visitors. A high conversion rate means your Marketing efforts and your offer are highly effective.

Example: If 100 people visit a page and 5 people buy the product, the conversion rate is 5%.
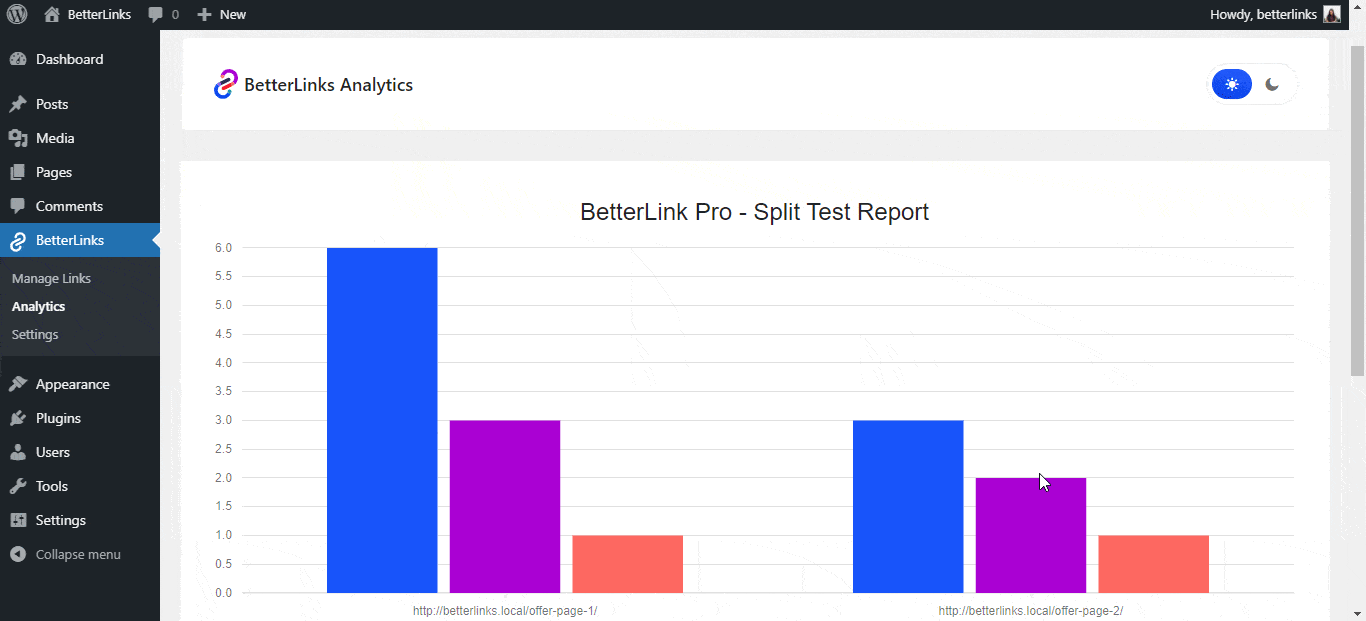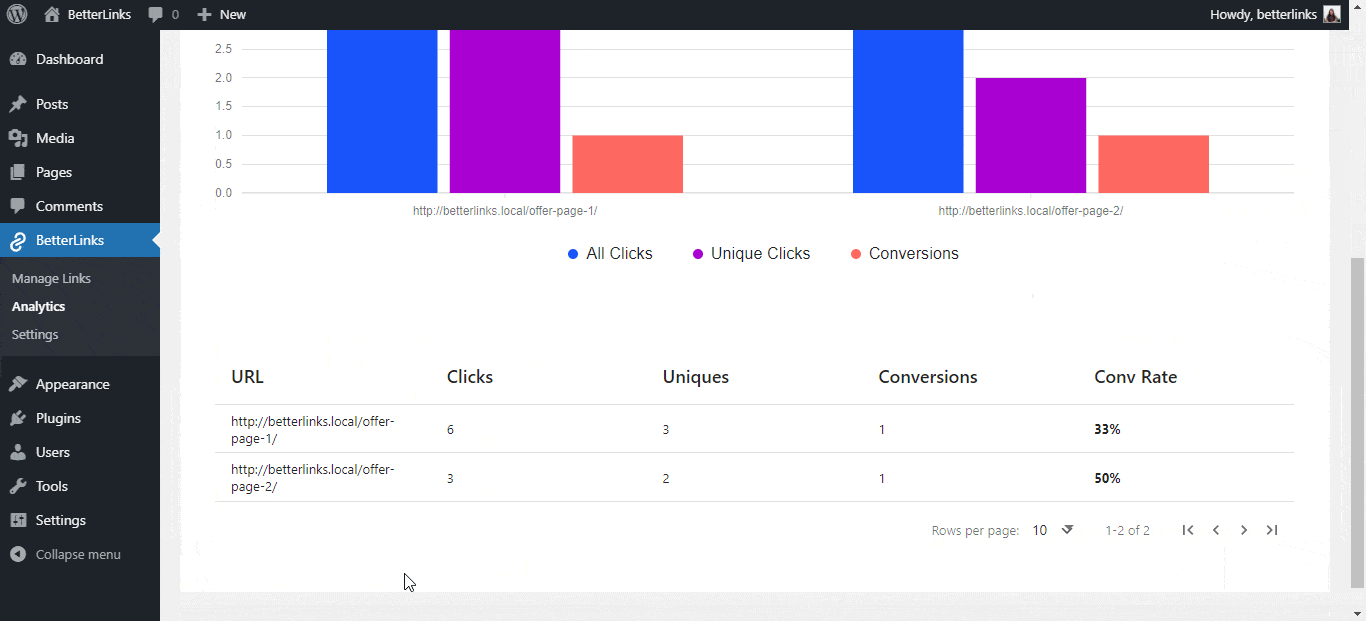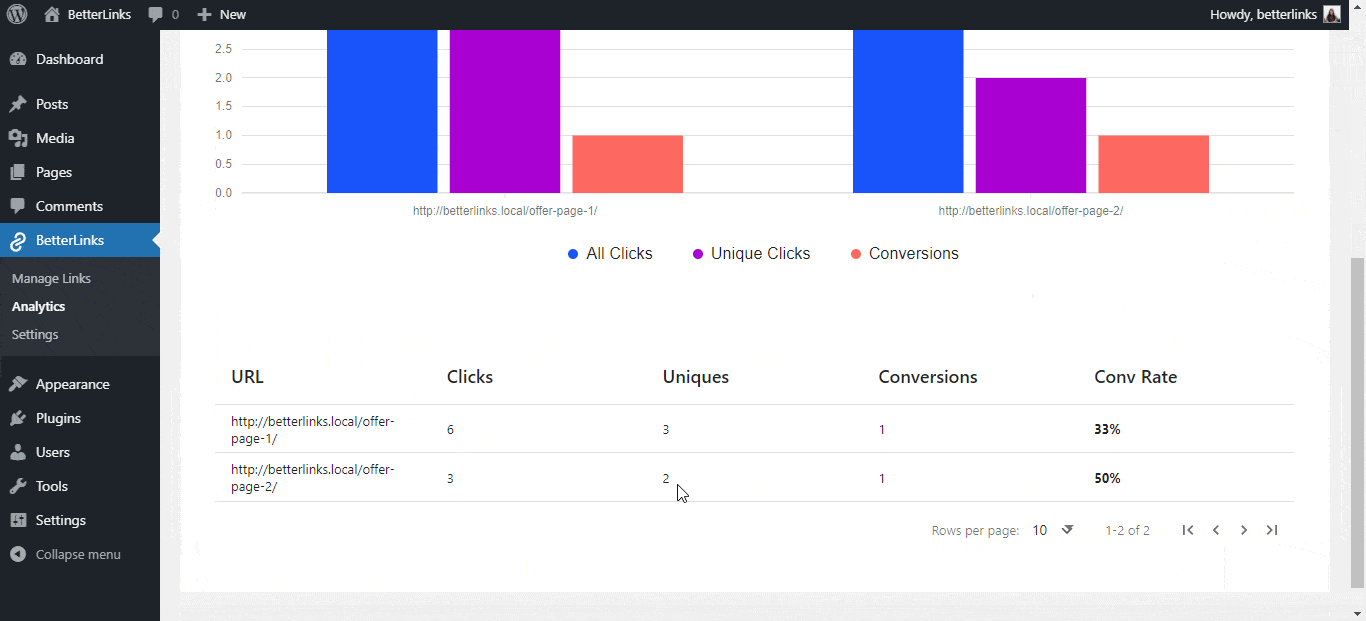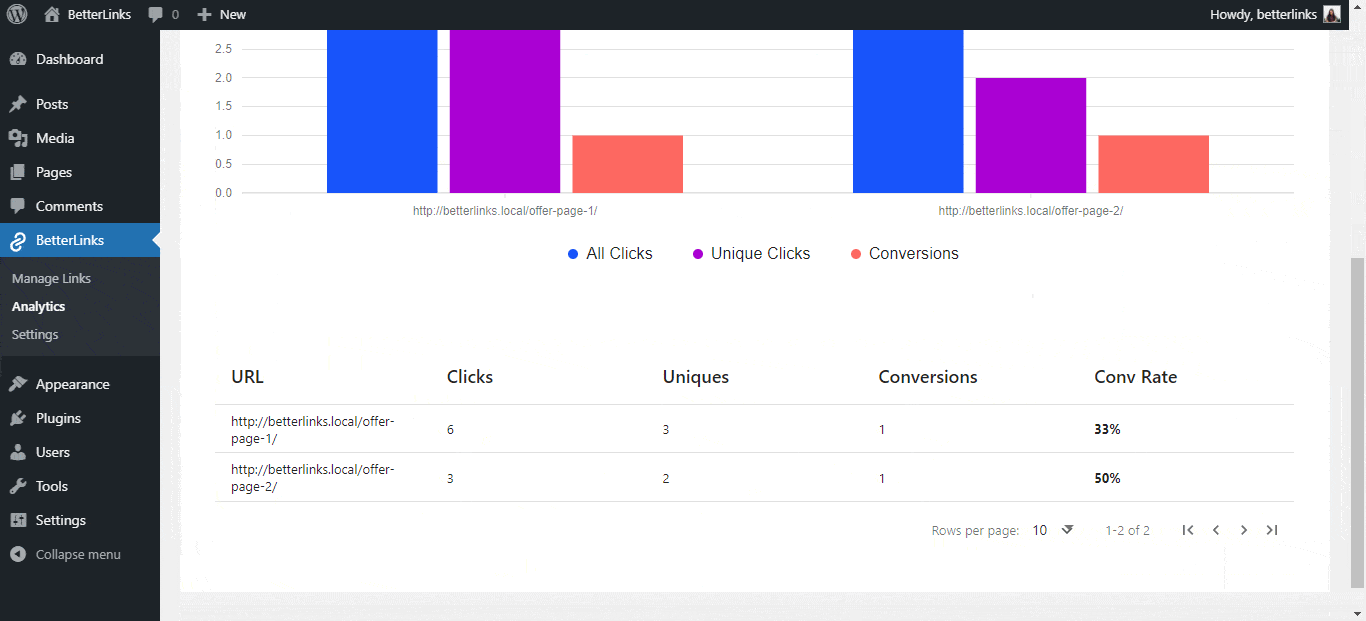
The ability to split-test landing pages with dynamic redirects in BetterLinks is a powerful way to continuously improve the conversion rate.
34. Impression
An impression is counted every time a promotional asset, like a banner or a text Affiliate Link, is displayed to a visitor. It measures the visibility of your promotion but not necessarily user engagement.
Example: A banner for a product is loaded on a visitor’s screen and counted as one impression.
35. Traffic Source
Traffic source is where your visitors are coming from, whether it is search engines, social media, email, or other websites. Knowing your best traffic sources is crucial for deciding where to invest your Marketing time and money.

Example: When users land on your site from platforms like Facebook, YouTube or Google, those platforms are considered traffic sources
36. A/B Testing or Split Testing
A/B testing is a method of comparing two versions of something, such as a landing page or a headline, to see which one performs better. This involves sending half your traffic to version A and half to version B.

Example: Testing two different headline styles on a review page to see which one generates more clicks on the Affiliate Link.
BetterLinks dynamic redirects allow for simple A/B testing of different destination URLs, ensuring you always use the highest converting link.
37. Tracking Pixel (Facebook Pixel)
A tracking pixel is a small piece of code placed on a website to collect data on visitors and their actions. This data is used to run retargeting campaigns or to better understand user behavior.

Example: Installing the Facebook Pixel on your WordPress site to track which users who clicked your Affiliate Link also viewed your checkout page.
38. Bot Blocking
Bot blocking is a security measure used to prevent automated software or non-human traffic from clicking Affiliate Links. Bots can skew analytics, waste bandwidth and in some cases trigger false sales.
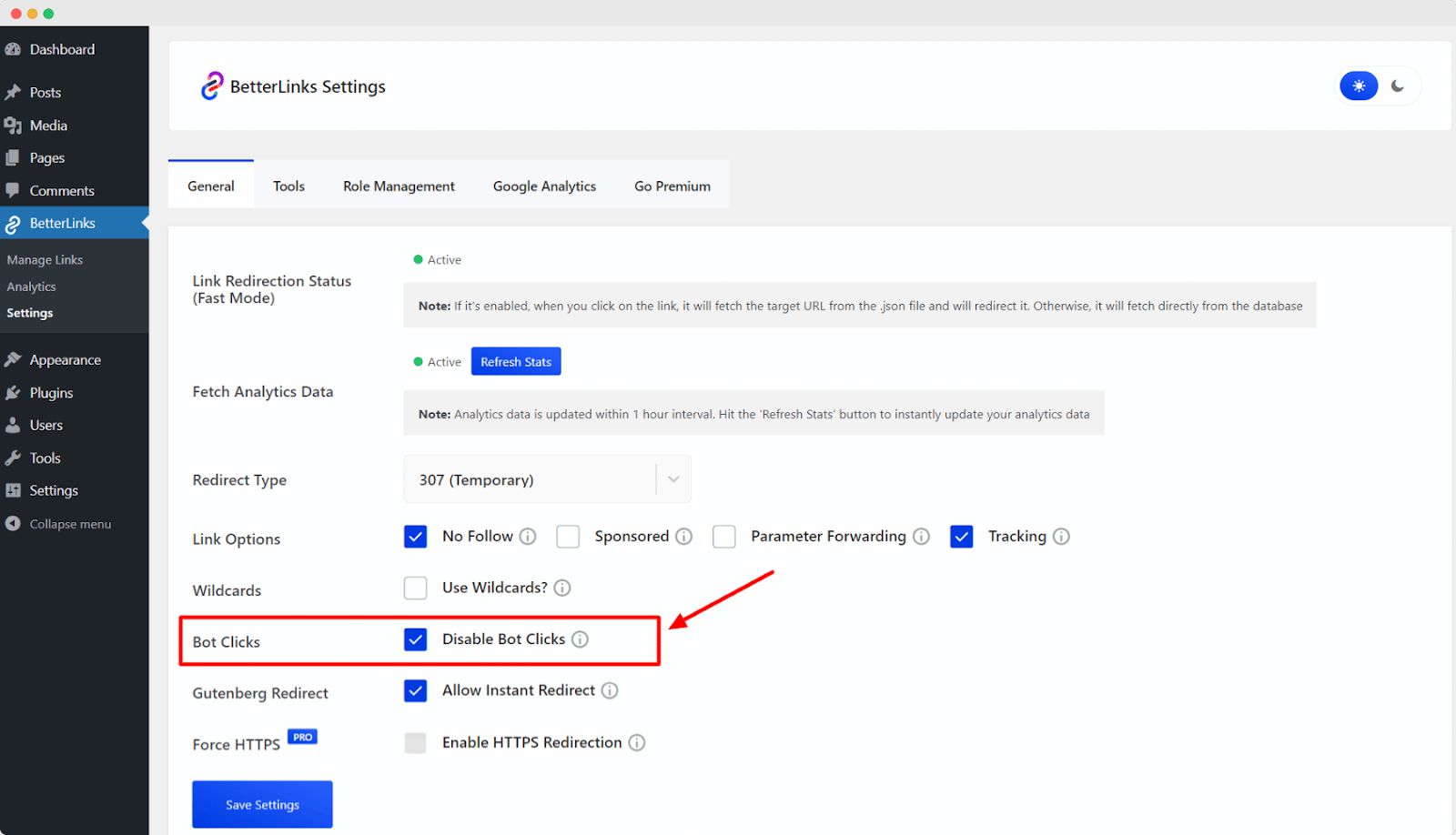
Example: An affiliate tool detects suspicious activity from a server farm and automatically blocks those clicks from being recorded.
BetterLinks includes bot-blocking features to ensure your click data is accurate and reliable, preventing fraud and skewed performance metrics.
39. Geotargeting
Geotargeting is the practice of delivering specific content or an Affiliate Link to a user based on their geographical location. This is important for promotions that are only valid in certain countries or regions.

Example: Sending a user from Canada to the Canadian version of a merchant’s site and a user from Australia to the Australian version.
BetterLinks allows for advanced redirection based on the user’s location, providing a localized and highly relevant user experience that boosts conversion.
40. Retargeting
Retargeting is a Marketing tactic that aims to bring back users who visited a website but did not complete a purchase or conversion. This is usually done by showing them targeted ads on social media or other websites.
Example: A user views a product on your site, then starts seeing ads for that same product on their Facebook feed through ads
41. Click Through Rate (CTR)
Click Through Rate (CTR) is the percentage of people who click on an Affiliate Link or advertisement after seeing it. It is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions. A high CTR indicates highly engaging content or placement.

Example: An email with an Affiliate Link is sent to 1000 people and 50 people click the link, resulting in a 5% CTR.
42. CPL (Cost Per Lead)
Cost Per Lead (CPL) is a pricing model where the affiliate is paid a commission for generating a qualified lead such as a user submitting a form, signing up for a trial or downloading gated content even if a sale has not been made yet. This is common for SaaS or B2B products focused on building funnels.
Example: A marketing software company pays the affiliate $10 for every user who completes the ‘request a demo’ form after clicking their Affiliate Link.
43. ROI (Return On Investment)
ROI is a fundamental metric that measures the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by comparing the net profit (total commissions) gained from a campaign against the total cost (paid traffic, content creation, tools, etc.) used to execute it. A positive ROI indicates a profitable campaign.
Example: An affiliate spends $500 on Facebook Ads (cost) and earns $1,500 in commissions (profit). The ROI is calculated as $(1500 – 500) / $500 = 2$, or 200%.
Compliance And Security Terms
Being a professional affiliate means adhering to legal and ethical standards. These Terms ensure you protect yourself, your audience and your commissions while maintaining good standing with search engines.
44. Disclosure
Disclosure is the mandatory practice of clearly telling your audience that you are being compensated for promoting a product or service. This is a legal requirement in many jurisdictions, like the FTC in the US and is crucial for maintaining trust.
Example: Adding a short sentence at the top of a review post like ‘This article contains Affiliate Links, which means I earn a small commission if you make a purchase.’
45. Nofollow Link Attribute
The nofollow attribute is a tag added to a hyperlink’s HTML code that tells search engines not to pass any SEO value or link equity to the destination page. Google recommends using nofollow or sponsored attributes on all paid Affiliate Links.
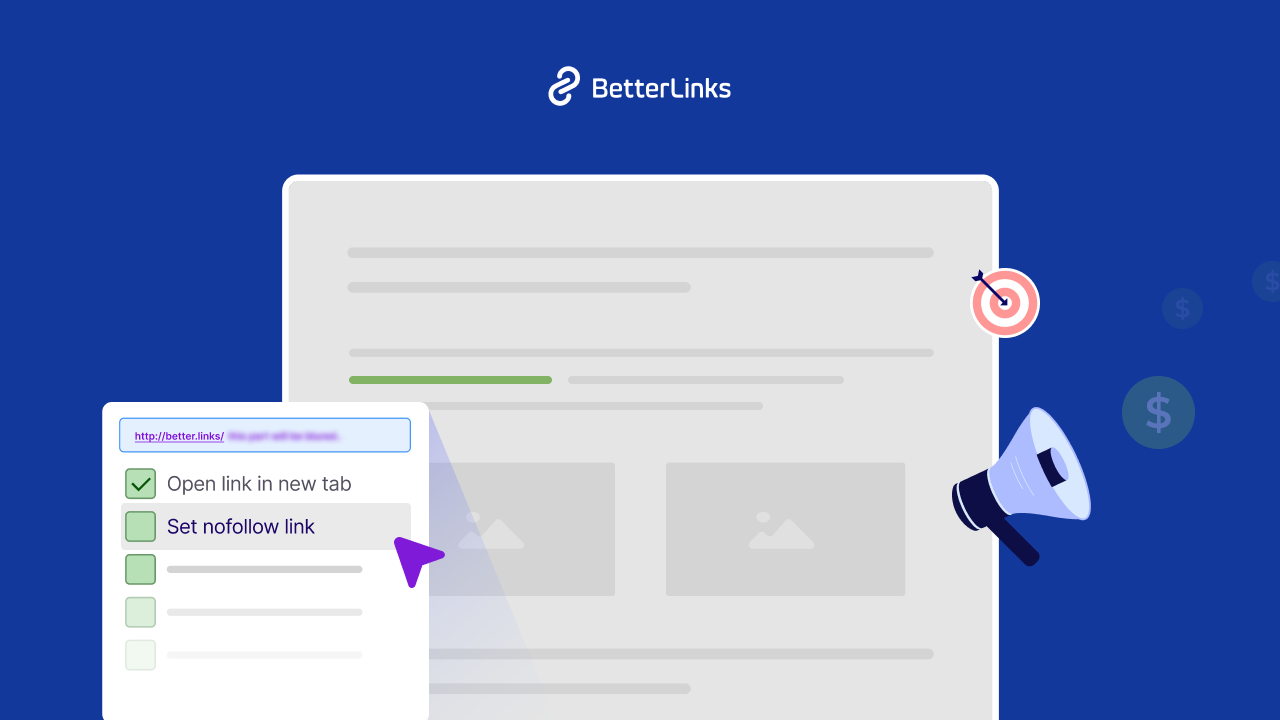
Example: <a href=”link.com” rel=”nofollow”>Product</a> is a nofollow link.
BetterLinks provides a simple toggle to add the nofollow or sponsored attribute to any Affiliate Link, ensuring full SEO compliance.
46. Sponsored Link Attribute
The sponsored attribute rel=”sponsored” is a newer link attribute specifically recommended by Google to identify links that were created as part of advertisements, sponsorships or other compensated agreements like Affiliate Marketing.
Example: <a href=”link.com” rel=”sponsored”>Product</a> clearly identifies the link as a paid promotion.
Along with nofollow, BetterLinks allows affiliates to easily apply the sponsored attribute to all their Affiliate Links for better SEO and compliance.
47. Terms of Service (TOS)
Terms of Service are the legal rules and conditions set by the merchant’s affiliate program. Affiliates must agree to these Terms to participate. Violating the TOS can lead to the affiliate being banned and losing all unpaid commissions.
Example: A TOS might forbid affiliates from bidding on the merchant’s brand-name keywords in search ads.
48. Brand Bidding
Brand bidding is the practice of bidding on a merchant’s trademarked name or branded keywords in pay-per-click campaigns like Google Ads. Most affiliate programs strictly forbid this practice as it directly competes with the merchant’s own ads.
Example: An affiliate tries to purchase a Google Ads placement for the keyword ‘Link Management WordPress Plugin’ but this violates the program’s TOS because the merchant does not allow affiliates to bid on branded or protected search terms.
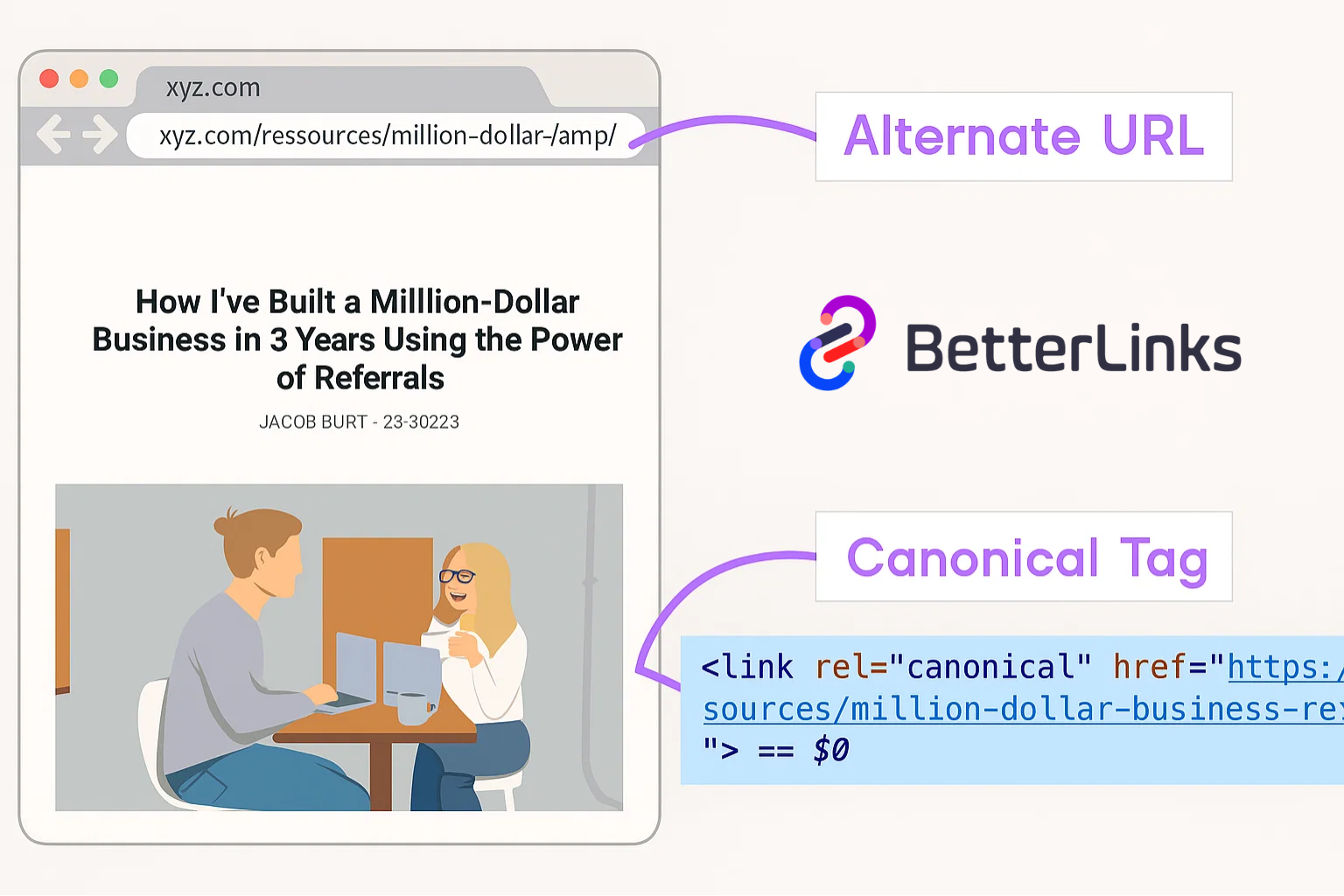
49. Canonical URL
A canonical URL is a tag that tells search engines which version of a page is the main or preferred version. This is important to prevent duplicate content issues, which can hurt SEO ranking.
Advanced Strategy And Marketing Terms
Go beyond the basics with advanced concepts that drive growth. These terms reveal how top affiliates scale earnings, refine funnels and stay ahead in a competitive market.
50. Marketing Funnel
A Marketing funnel is the theoretical path a customer takes from becoming aware of a product to making a purchase. It typically involves stages like Awareness, Interest, Desire and Action. Affiliates create content designed for each stage of the funnel.

Example: A blog post is for the Awareness stage, while an email sequence is for the Desire stage.
By scheduling links and setting click limits, BetterLinks helps affiliates manage scarcity and offers effectively at the bottom of the funnel.
51. Sub ID or Tracking ID
A Sub ID is an optional unique identifier that the affiliate can add to their Affiliate Link to track clicks and conversions from specific sources. This is used for granular campaign analysis beyond standard UTM parameters.
Example: The affiliate adds &subid=homepage_banner to the link to know exactly how many sales came from that specific banner placement.
BetterLinks provides easy ways to generate and manage dynamic tracking parameters, including Sub IDs for sophisticated campaign tracking.
52. Tiered Commission
A tiered commission structure rewards affiliates with higher commission rates as they hit specific sales volumes or performance targets. This motivates affiliates to drive more traffic and sales.
Example: An affiliate earns 20% commission until they hit 50 sales, then their rate increases to 25%.
53. Lifetime Value (LTV)
Customer Lifetime Value or LTV is the total amount of money a customer is expected to spend with the merchant over the entire time they are a customer. Affiliates often look for programs with high LTV, especially those with recurring commissions.
Example: A customer who signs up for a $100 per month tool and stays subscribed for 5 years has an LTV of $6000.
When an affiliate uses a platform for Affiliate Link Management with long-term tracking, they can confidently invest in high LTV offers.
54. Vanity URL
A vanity URL is a unique, memorable and branded web address that is easy to share. It is a short link created to replace a long, complex URL. This is a crucial element for strong Marketing and brand recognition.
Example: yourdomain.com/go/besttool is a vanity URL that uses the brand’s domain.
55. Opt-in Rate
Opt-in rate is the percentage of visitors to a squeeze page or content upgrade who successfully submit their email address and become a lead (opt-in). This metric measures the effectiveness of the lead magnet and the landing page design.
Example: If 100 people visit a squeeze page and 30 people enter their email, the opt-in rate is 30%.
56. Pay Per Click (PPC) / SEM
Pay Per Click (PPC) is a Marketing model where advertisers pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. Search Engine Marketing (SEM) uses paid advertising (like Google Ads) to increase website visibility in search results. Affiliates use PPC to drive targeted traffic to their bridge pages or reviews.

Example: Running a Google Ad campaign targeting the keyword ‘cheap hosting alternatives’ to drive traffic to a review page containing Affiliate Links.
57. Daily Budget
A daily budget is the maximum amount of money an affiliate is willing to spend per day on paid traffic sources, such as PPC ads or social media promotions. It is a key control mechanism used to limit financial risk and scale campaigns predictably.
Example: An affiliate sets a daily budget of $20 for a Google Ads campaign promoting a specific product review to ensure they do not overspend before optimizing the conversion rate.
58. Viral Marketing
Viral Marketing is a Marketing strategy that encourages individuals to pass along a promotional message or piece of content to others, often resulting in exponential growth in reach and brand awareness. It leverages the enthusiasm of early adopters and the power of word-of-mouth.
Example: An affiliate creates a highly humorous or intensely useful piece of content (like a quiz or a controversial guide) related to the product they are promoting, causing followers to spontaneously share it across social media.
From Glossary to Growth: Step Into Affiliate Success Today
You have explored 50+ key affiliate marketing terms, your foundation for success in 2026. But learning is just the start. Apply these concepts by managing links, tracking metrics and optimizing with plugins like BetterLinks. Stay curious, keep learning and turn knowledge into action. Success comes to affiliates who combine technical skills with consistent effort and genuine value for their audience.
Is this blog helpful? Join our community to stay updated with the latest blogs, product reviews and WordPress solutions. Subscribe to our blog for in-depth tutorials, tips and product demos, or visit our website for the newest updates.




