Do you have a well-optimized consistent WordPress site yet wonder what is missing? The answer is technical SEO. Because technical SEO for WordPress is the backbone of your website’s performance and visibility on search engines, it ensures that your site is not only accessible to search engines but also provides a seamless experience for users. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the aspects of technical SEO for WordPress to understand it better and implement them.

Understanding Technical SEO

Technical SEO is optimizing your website’s infrastructure to ensure it is easily accessible, understandable, and indexable by search engines. Technical SEO focuses on the backend elements of your site, such as server configurations, site architecture, and code optimization. Altogether to improve the site visibility and performance on search engines.
In the broader SEO strategy, technical SEO plays a crucial role. It ensures that search engines can crawl and index your site efficiently since it helps your content to appear in search results. Without proper technical SEO for WordPress sites, even the most compelling content might remain hidden from your audience. It acts as the first step in a comprehensive SEO campaign, laying the groundwork for other SEO efforts like on-page and off-page optimization.
Key Components Of Technical SEO For WordPress
Technical SEO for WordPress involves optimizing various backend elements to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank your site. Key components include:
Crawling
Crawling is the process by which search engine bots, navigate through your website to discover new and updated content. These bots follow links from one page to another, creating a map of your site. Ensuring that your site is easily crawlable. It is vital because if the bots cannot find your pages, they cannot index them. You can utilize crawling by maintaining a clean and logical site structure. Also by using internal links effectively, and creating an XML sitemap.
Indexing
Once the bots have crawled your site, the next step is indexing. Indexing involves storing and organizing the content found during the crawl so that it can be retrieved during a search query. If your pages are not indexed, they will not appear in search results. To optimize for indexing, ensure that your site does not have duplicate content. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page, and avoid using “noindex” tags on important pages.
Site Architecture
Site architecture refers to the way your website is structured and how its pages are interconnected. A well-organized site architecture helps both users and search engines navigate your site more efficiently. It involves creating a logical hierarchy of pages, using breadcrumb navigation, and ensuring that all important pages are easily accessible from the homepage. Good site architecture improves crawlability, enhances user experience, and helps distribute link equity throughout your site.
Page Speed
Page speed is a critical component of technical SEO. It directly affects user experience and search engine rankings. Faster-loading pages lead to lower bounce rates and higher user engagement. Search engines like Google use page speed as a ranking factor, meaning that slow-loading pages can negatively impact your search rankings. To optimize page speed, you can use browser caching, compress images, and minify CSS and JavaScript files. Also, you can use a content delivery network (CDN) to reduce server load times.
Why Technical SEO is Crucial for WordPress Sites
Technical SEO directly impacts user experience by improving site speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall usability. Fast-loading pages and a mobile-friendly design are critical as they reduce bounce rates and increase user engagement, both of which are important ranking factors. Tools and plugins can help optimize these aspects, making your site more appealing to both users and search engines.
A well-optimized WordPress site can give you a competitive edge. By addressing technical SEO issues, you can achieve higher rankings than competitors who may overlook these details. This not only drives more organic traffic to your site but also builds credibility and trust with your audience, leading to better engagement and higher conversion rates.
Core Elements of Technical SEO for WordPress

To ensure your WordPress site performs optimally in search engine rankings, it is crucial to focus on several core elements of technical SEO. Such as:
Flat and Organized Site Structure
A flat and organized site structure is crucial for both user experience and SEO. In a flat hierarchy, each page is accessible within a few clicks from the homepage. It simplifies navigation for users and ensures that search engines can easily crawl and index your content. This structure minimizes the number of clicks needed to reach deeper pages, making important content more accessible and improving overall site performance. Here are some ways to maintain an organized site structure:
- Logical Information Architecture: Organize your content into clear categories and subcategories. This helps both users and search engines understand the structure of your site.
- Breadcrumbs: Use breadcrumb navigation to enhance user experience and provide additional internal links for search engines.
- Internal Linking: Ensure that all important pages are interlinked. This not only helps users navigate but also distributes link equity throughout your site.
- URL Structure: Use descriptive and keyword-rich URLs that are easy to read and understand.
Crawling and Indexing

Crawling is the process by which search engine bots, like Googlebot, systematically browse the internet to discover and access web pages. Indexing follows crawling and involves storing and organizing the content found during crawling in a search engine’s database. This indexed content is then used to provide relevant search results to users.
- XML Sitemaps: Create and submit an XML sitemap to guide search engines to all your important pages.
- Robots.txt File: Optimize your robots.txt file to ensure it does not block important pages from being crawled.
- Internal Links: Use a strong internal linking strategy to help search engines discover all pages on your site.
- Avoid Duplicate Content: Ensure that your site does not have duplicate content, as this can confuse search engines and lead to indexing issues.
XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps act as a roadmap for search engines, helping them find and crawl all important pages on your site. They are particularly useful for large websites, new websites with few external links, and sites with rich media content. An XML sitemap can improve the efficiency of the crawling process and ensure that all critical pages are indexed. Create and submit sitemaps in WordPress in the following ways:
- Using Plugins: Plugins like Rank Math can automatically generate XML sitemaps for your WordPress site. These plugins also offer options to customize which content is included in the sitemap.
- Manual Submission: After generating the sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console and other search engines to ensure it is recognized and used for crawling.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is used to control how search engine bots crawl and index your site. Proper configuration can prevent bots from wasting resources on non-essential pages and ensure they focus on important content. To keep robots.txt optimized the best practices could be:
- User-Agent Specification: Tailor instructions for different search engine bots using “User-Agent” directives.
- Disallow Directives: Use the “Disallow” directive to block bots from crawling non-essential sections like admin panels and login pages.
- Allow Directives: Explicitly allow access to critical pages to ensure comprehensive indexing.
- Sitemap Declaration: Include the location of your XML sitemap in the robots.txt file to guide search engines.
Robots.txt Examples
Allow All Crawlers Access to Everything
This configuration allows all web crawlers to access and index all parts of the website.
text
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Disallow All Crawlers from Everything
This configuration blocks all web crawlers from accessing any part of the website.
text
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Allow All Crawlers and Specify Sitemap
This configuration allows all web crawlers to access the entire site and provides the location of the sitemap.
text
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Block Specific Crawlers from Specific Directories
This configuration blocks Googlebot from accessing the /shoes/ directory and Bingbot from accessing the /socks/ directory.
text
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /shoes/
Enhancing Site Performance

Fast-loading pages are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they significantly impact user experience. Users are more likely to abandon a site if it takes more than a few seconds to load, leading to higher bounce rates. Secondly, page speed is a critical factor in search engine optimization (SEO). Google uses page speed as a ranking factor, meaning slower pages are likely to rank lower in search results. Finally, faster pages can lead to higher conversion rates, as users are more likely to engage with and complete actions on a site that loads quickly.
Techniques for Improving Page Speed
- Caching: Implementing caching mechanisms can store copies of your site’s pages, reducing the load time for returning visitors. Tools like WP Rocket can help with this.
- Image Optimization: The Elementor Image Optimizer plugin is a powerful tool for enhancing website performance and load times. This plugin automatically compresses and resizes images upon upload, and supports popular formats. By reducing image file sizes and improving overall site performance, the Elementor Image Optimizer can significantly boost page load speeds.
- Minimizing CSS and JavaScript: Reducing the size of CSS and JavaScript files by minifying them can decrease load times. Combining multiple files into one can also reduce HTTP requests. Using WP Rocket can boost the workflow in this case.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Using a CDN can distribute your content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing latency and speeding up load times for users regardless of their location.
Mobile Optimization
Mobile-first indexing means that Google predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. This shift reflects the growing number of users accessing the internet via mobile devices. If your site is not optimized for mobile, it could negatively impact your search rankings and user experience.
Tips for Making Your WordPress Site Mobile-Friendly
Following the recent updates made by Google it is clear that mobile-optimized sites would get priority in certain aspects on SERP, so, here’s some tips to follow by:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your site uses a responsive design that adapts to various screen sizes. Most modern WordPress themes are responsive by default.
- Google AMP: Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) can help create fast-loading mobile pages. Implementing AMP can improve load times and user experience on mobile devices.
- Mobile–Optimized Plugins: Use plugins that are optimized for mobile performance like WPtouch. Avoid using Flash and ensure that all interactive elements work smoothly on mobile devices.
- Consistent Content: Ensure that the content on your mobile site is consistent with your desktop site. Use techniques like accordions and tabs to manage content effectively on smaller screens.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics defined by Google to measure the user experience of a web page. They focus on three main aspects:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. A good LCP score is 2.5 seconds or less.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures interactivity. A good INP score is 200 milliseconds or less.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. A good CLS score is 0.1 or less.
Strategies for Optimizing These Metrics
- Improving LCP: Optimize server response times, use a CDN, and ensure that the largest content elements load quickly. This can include optimizing images and removing render-blocking resources.
- Enhancing INP: Minimize JavaScript execution time, reduce the impact of third-party code, and ensure that the main thread is not blocked during user interactions.
- Reducing CLS: Use size attributes for images and videos to prevent layout shifts, and avoid inserting content above existing content unless it is in response to user interaction
Security and HTTPS

HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is essential for both SEO and user trust. Here are the key reasons why:
SEO Benefits
Search engines like Google prioritize websites that use HTTPS over those that use HTTP. This is because HTTPS ensures that the data exchanged between the user’s browser and the website is encrypted and secure. Google has made HTTPS a ranking signal, meaning that sites with HTTPS are more likely to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This can lead to increased visibility and more organic traffic.
User Trust and Credibility
Users are more likely to trust and engage with websites that are secure. When a website uses HTTPS, it displays a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, signaling to users that their data is protected. This can enhance user confidence, reduce bounce rates, and increase the time spent on the site. In contrast, websites that do not use HTTPS may be marked as “not secure,” which can deter users from interacting with the site.
Steps to Implement HTTPS on Your WordPress Site
Implementing HTTPS on a WordPress site involves several steps:
- Obtain an SSL Certificate: The first step is to acquire an SSL certificate. Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through encryption. You can also purchase an SSL certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Install the SSL Certificate: Once you have the SSL certificate, you need to install it on your web server. This process varies depending on your hosting provider, but most offer straightforward guides or support to help you through the installation.
- Update WordPress Settings: In your WordPress dashboard, navigate to Settings > General. Update the WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) fields to use https instead of http. Save the changes.
- Set Up Redirects: To ensure that all traffic is redirected from HTTP to HTTPS, you need to set up redirects. This can be done by adding the following code to your .htaccess file for Apache servers:
text
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
</IfModule>
For NGINX servers, add the following to your configuration file:
text
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
- Replace example.com with your domain name.
- Update Links and Resources: Ensure that all internal links and resources (such as images, scripts, and stylesheets) use HTTPS. You can use plugins like “Better Search Replace” to update URLs in your database.
- Force SSL in Admin Area: To secure your WordPress admin area, add the following line to your wp-config.php file:
php
define(‘FORCE_SSL_ADMIN’, true);
- This ensures that your admin pages are always loaded over HTTPS.
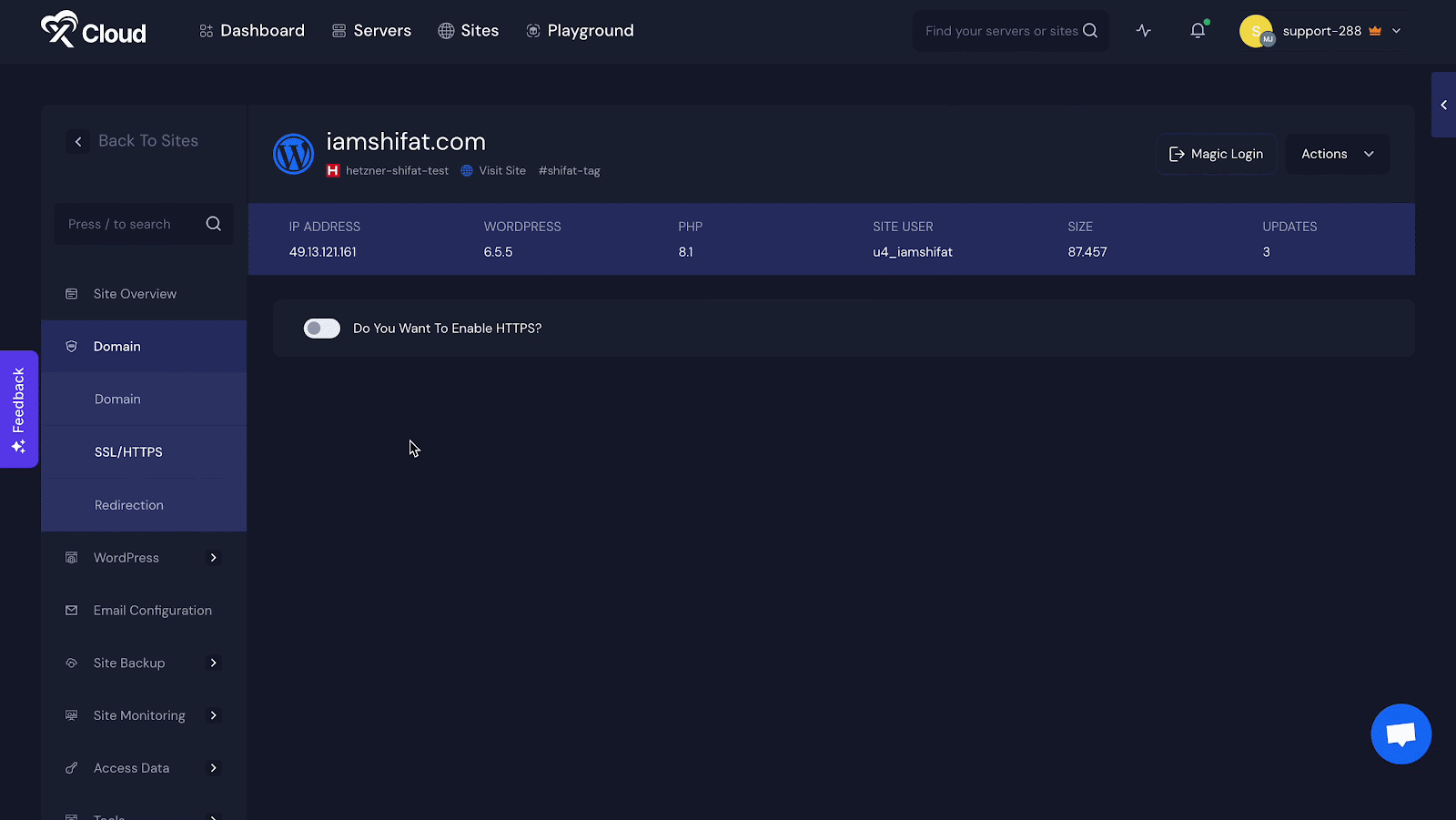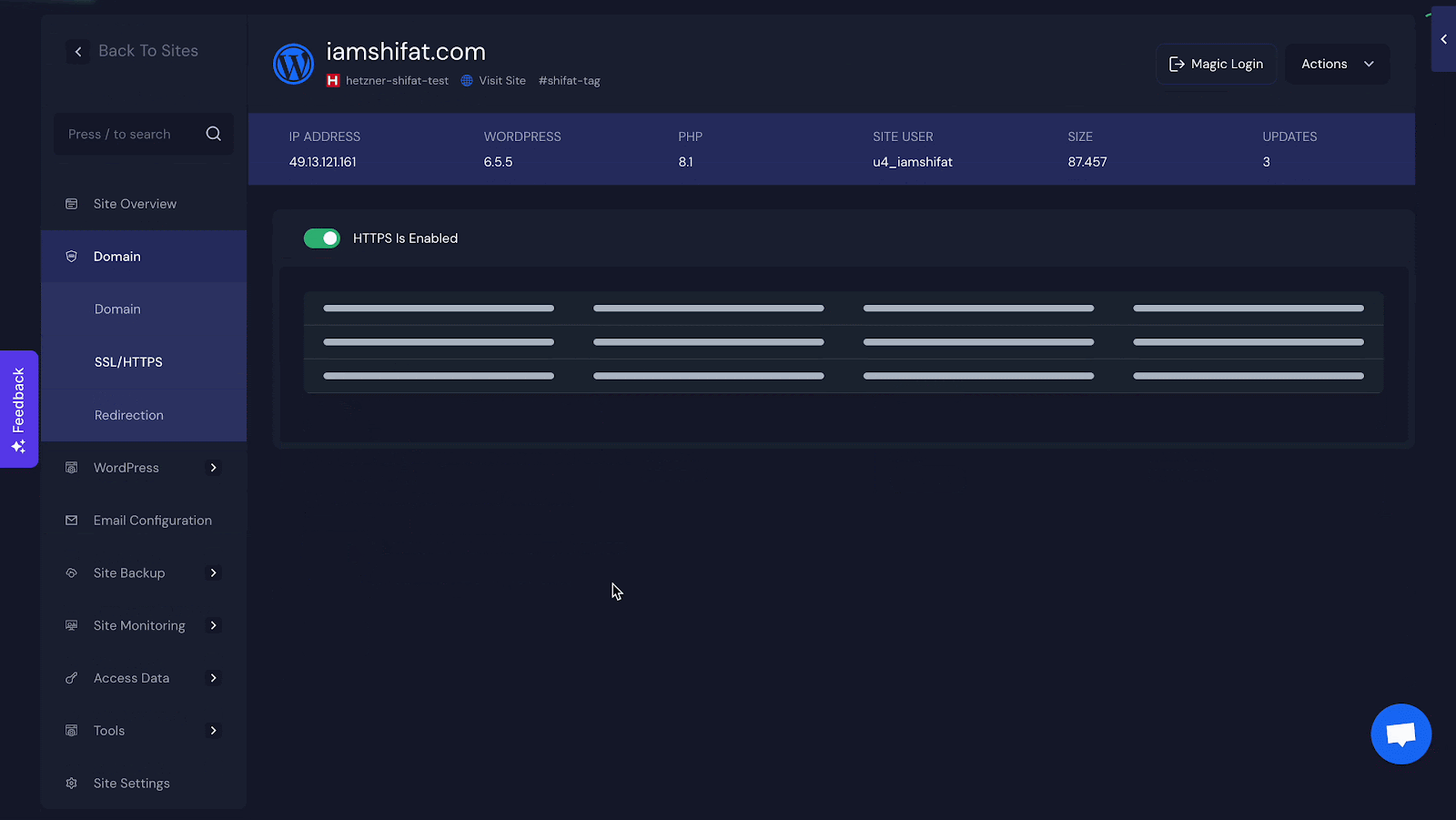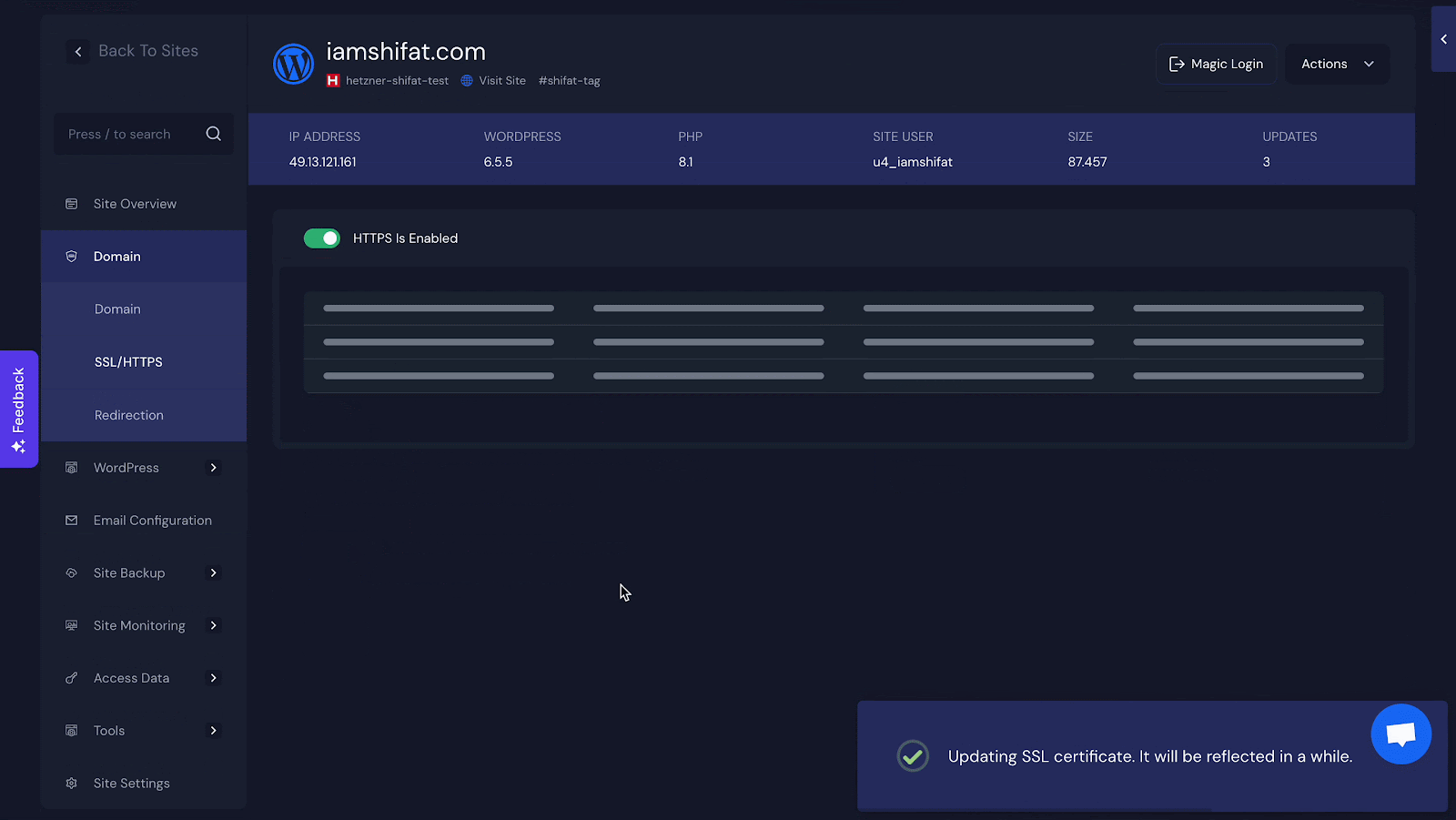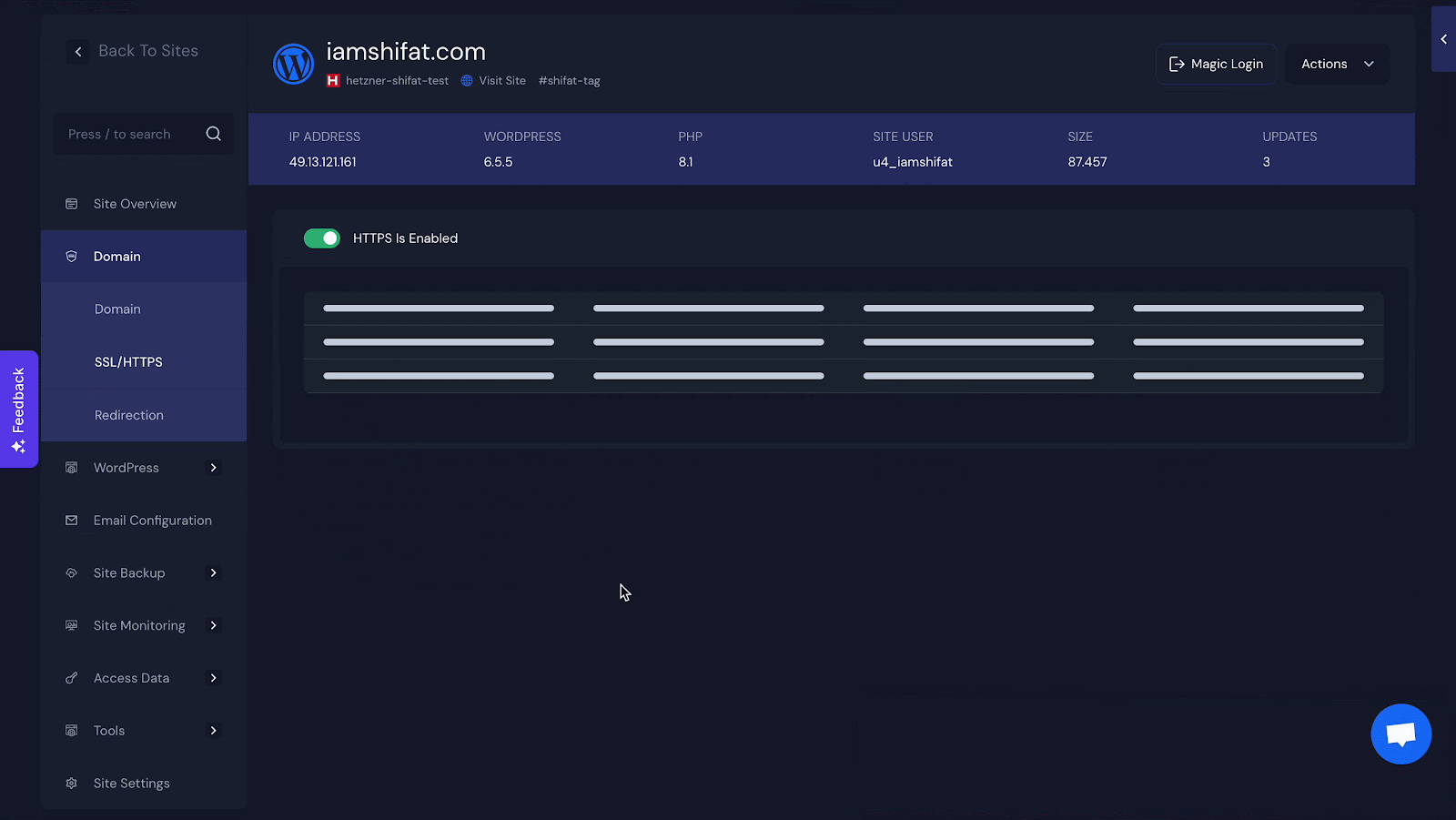
However, you can do all the SSL certificate tasks and redirection with xCloud for your WordPress site easily. Take a look at how easy it is to install an SSL certificate in xCloud?
Security Best Practices

Keeping WordPress, along with its themes and plugins, up to date is crucial for security. Outdated software can have vulnerabilities that hackers exploit. Regularly check for updates and apply them promptly. You can enable automatic updates for plugins to ensure they are always up to date.
Regular backups are essential to safeguard your data. In case of a security breach or malfunction, having a recent backup allows you to restore your site quickly. Use plugins like Jetpack VaultPress Backup to automate backups and store them off-site for added security.
Using Security Plugins and Monitoring Tools
- Security Plugins: Installing a reputable security plugin can provide comprehensive protection for your WordPress site. Plugins like Jetpack Security offer features such as spam protection, DDoS attack protection, malware scanning, and a web application firewall (WAF). These tools help monitor and secure your site against various threats.
- Monitoring Tools: Regularly monitor your website for suspicious activity. Security plugins often include monitoring tools that alert you to potential issues. Additionally, services like Google Search Console can notify you of any security problems detected on your site.
Handling Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to blocks of text that appear in more than one location on the internet, either within the same website or across different websites. This can significantly harm SEO in several ways:
- Confusion for Search Engines: When search engines encounter duplicate content, they struggle to determine which version is the original or most relevant. This can lead to lower rankings for all versions of the content, as search engines may not know which one to prioritize.
- Diluted Link Equity: If multiple pages with similar content receive backlinks, the link equity is spread across these pages rather than being concentrated on a single authoritative page. This dilution can weaken the overall SEO strength of the content.
- Reduced Crawl Efficiency: Search engines have a limited crawl budget for each site. Duplicate content can waste this budget, leading to fewer unique pages being indexed and potentially missing out on important content.
- Potential Penalties: Although rare, in extreme cases where duplicate content is deemed to be manipulative, search engines like Google may impose penalties or even deindex the offending site.
Tools and techniques for identifying and resolving duplicate content issues
Identifying and resolving duplicate content is crucial for maintaining good SEO health. Here are some tools and techniques:
- Google Search Console: This tool can help you identify duplicate content issues by showing you which pages are indexed and highlighting any anomalies.
- 301 Redirects: Implementing 301 redirects from duplicate pages to the original page can help consolidate link equity and direct search engines to the correct version.
- Content Rewriting: For pages with similar content, consider rewriting the text to make each page unique. This is especially important for e-Commerce sites with similar product descriptions.
- Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page to search engines. This helps consolidate duplicate content issues by pointing to the master copy.
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are HTML elements used to prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the “canonical” or preferred version of a web page. Here is a detailed explanation of their usage:
A canonical tag (rel=”canonical”) is a snippet of HTML code that tells search engines which version of a page should be considered the main one. This is particularly useful when you have multiple URLs with similar or identical content.
xml
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/preferred-page/” />
Canonical tags help consolidate duplicate content issues by directing search engines to the preferred version of a page. This ensures that all link equity and ranking signals are attributed to the main page, improving its chances of ranking higher in search results.
To use Rank Math for setting canonical tags easily. Install and activate the Rank Math SEO plugin on your WordPress site. Edit the post or page where you want to set the canonical URL. Scroll down to the Rank Math SEO settings section below the content editor.
Click on the “Advanced” tab within the Rank Math meta box. Locate the “Canonical URL” field in the Advanced settings. Enter the preferred canonical URL for the page in this field. Save or update the post/page. By default, Rank Math uses the current post/page URL as the canonical URL, so you only need to change this setting if you want to specify a different canonical URL
Best Practices for Implementing Canonical Tags
- Use Absolute URLs: Always use absolute URLs in your canonical tags to avoid confusion. For example, use https://example.com/page instead of /page.
- Self-Referencing Canonical Tags: Even if a page does not have duplicates, it is a good practice to include a self-referencing canonical tag to prevent future issues.
- Consistent Use: Ensure that canonical tags are used consistently across your site, especially on dynamic pages generated by CMS or e-commerce platforms.
- Avoid Mixed Signals: Do not mix canonical tags with other signals like 301 redirects or meta noindex tags, as this can confuse search engines
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data and schema markup are essential tools for enhancing the visibility and performance of your website in search engine results. By providing a clear and organized way for search engines to understand your content, you can improve your site’s SEO and user experience.
Structured Data Helps Search Engines Understand Your Content. It helps search engines like Google understand the context and meaning of your content, which can lead to more accurate and relevant search results. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Search Engine Visibility: Structured data helps search engines index your content more effectively, making it easier for them to display your site in relevant search results.
- Enhanced Search Results: By using structured data, your content can appear as rich snippets, which include additional information such as ratings, prices, or images directly in the search results. This can make your listing more attractive and informative to users.
- Increased Click-Through Rates (CTR): Rich snippets and other enhanced search results can lead to higher CTRs because they provide users with more information upfront, making them more likely to click on your link.
- Better User Experience: Structured data can improve the user experience by providing quick answers and relevant information directly in the search results, reducing the need for users to click through multiple pages to find what they need.
Types of Schema Markup Relevant for WordPress Sites
Numerous types of schema markup can be implemented on WordPress sites, each serving different purposes. Some of the most relevant types include:
- Article: Useful for blog posts and news articles.
- Product: Ideal for e-Commerce sites to describe products, including details like price, availability, and reviews.
- Recipe: Perfect for food blogs to display ingredients, cooking times, and nutritional information.
- Local Business: Helps local businesses provide information like address, phone number, and opening hours.
- FAQ: Allows you to mark up frequently asked questions and their answers.
- HowTo: Useful for step-by-step guides and tutorials.
- Event: For promoting events with details like date, location, and ticket information.
Tools and Plugins for Adding Structured Data to WordPress
Implementing structured data on a WordPress site can be straightforward, especially with the help of various plugins. Here are some popular tools and plugins you can use:
- Schema & Structured Data for WP & AMP: This plugin supports over 35 schema types and is compatible with AMP. It allows you to include or exclude specific posts, pages, and taxonomies, and it offers advanced settings for customizing the output of schema markup.
- Schema Plugin: A lightweight plugin that automatically adds schema.org structured data markup in JSON-LD format. It supports various schema types and is easy to use with minimal settings.
- WP SEO Structured Data Schema: This plugin provides flexibility and manual customization options for adding schema markup. It supports custom post types and allows you to add schema on a page-by-page basis.
- Rank Math: Another feature-rich SEO plugin that offers extensive schema markup functionality. It includes a built-in Schema Generator and supports multiple schema types for individual posts and pages.
Common Technical SEO Issues in WordPress and How to Fix Them
WordPress is a powerful and flexible content management system (CMS), but it is not without its technical SEO challenges. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining a healthy website and improving search engine rankings. Here are some common technical SEO issues in WordPress and how to fix them.
Identifying & Fixing Broken Links

Broken links, also known as dead links, occur when a URL points to a page that no longer exists. These can negatively impact user experience and SEO rankings. Fortunately, there are several ways to identify and fix broken links in WordPress:
Google Search Console: Connect your site to Google Search Console to receive reports on broken links and other SEO issues. Navigate to the Coverage tab to see a list of errors, including 404 errors.
External Tools: Tools like BetterLinks offer a powerful broken link checker feature for WordPress sites. It allows one-click scanning of your entire website, providing detailed reports on broken URLs. The tool enables easy management and fixing of broken links directly from the WordPress dashboard. With scheduled scans and email notifications, BetterLinks helps maintain link health and improve user experience.
Once identified, you can fix broken links by setting up 301 redirects to relevant pages using BetterLinks.
Creating Custom 404 Pages

A custom 404 page can enhance the user experience by providing helpful navigation options when a user encounters a broken link. Here is how to create a custom 404 page in WordPress:
1. Create a New Page: Go to Pages and, Add New in your WordPress dashboard and create a new page with a user-friendly message and helpful links.
2. Edit 404 Template: Access your theme’s 404.php file via Appearance to the Theme Editor. Replace the default content with the content of your new page.
3. Use a Plugin: Alternatively, use a plugin like 404page to easily set a custom 404 page without editing code.
Best Practices for Image & Video Optimization
Optimizing media files is essential for improving site speed and SEO. Here are some best practices:
- Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or plugins like Smush and ShortPixel to compress images without losing quality.
- Resize Images: Ensure your images are appropriately sized for their use. You can set maximum dimensions in Settings then select, Media.
- Use Appropriate Formats: Use JPEG for photographs and PNG for graphics with transparent backgrounds. For videos, use MP4 with H.264 codec for the best balance between quality and file size.
- Lazy Loading: Enable lazy loading for images and videos to improve initial page load times. This can be done using plugins like Lazy Load by WP Rocket.
Ensuring All Media Files Have Appropriate Alt Attributes
Alt attributes provide descriptions for images, which help with accessibility and SEO. Here is how to add alt text to images in WordPress:
1. Add During Upload: When uploading an image, fill in the Alt Text field in the media uploader.
2. Edit Existing Images: Go to Media, then click on, ‘Library’, select an image, and add alt text in the Alt Text field on the right-hand side.
3. Use Plugins: Plugins like Yoast SEO can help ensure all images have alt text by providing reminders and fields for alt text during content creation.
Tools and Resources for Technical SEO
Mastering technical SEO requires the right combination of tools and resources. Essential SEO plugins like Yoast SEO and RankMath have robust features for optimizing site performance. Conducting thorough technical audits is made easier with tools such as Google Search Console, Semrush, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs, each providing unique insights and actionable recommendations. Utilizing these tools and resources effectively can significantly enhance your website’s SEO performance.
We hope you found this blog helpful and If you want to read more exciting blogs, subscribe to our blog page, and join our Facebook community to get along with all WordPress experts.




