When you build a website, creating content is just the first step. You also need to connect your pages properly using links. These connections help both your visitors and search engines understand your site better. But not all links are the same. Some point to pages within your own website while others lead to different websites entirely.

Links are the foundation of the internet. They create pathways that guide users from one piece of information to another. For website owners, knowing how to use internal links and external links correctly is essential for success. Both types serve unique purposes and offer different benefits.
This guide will explain everything you need to know about internal links vs external links. You will learn what makes them different, why they matter for SEO and how to use them effectively on your website.
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of your website to another page on the same domain. These links create a network of connected pages that help visitors navigate your site easily.

Think of internal links as hallways in a building. They guide people from one room to another without making them leave the building. Every time you link from your homepage to your about page or from one blog post to another related article, you are creating an internal link. These connections are completely within your control because they only involve pages you own.
Internal links serve multiple purposes that benefit both your visitors and your website’s search engine performance. They make navigation simpler, spread link value across your pages and help search engines discover and understand your content structure.
What Are External Links?
External links are hyperlinks that point from your website to a different domain. When someone clicks an external link on your site, they leave your website and land on someone else’s page. These links connect your content to resources, references and information that exist outside your own site.
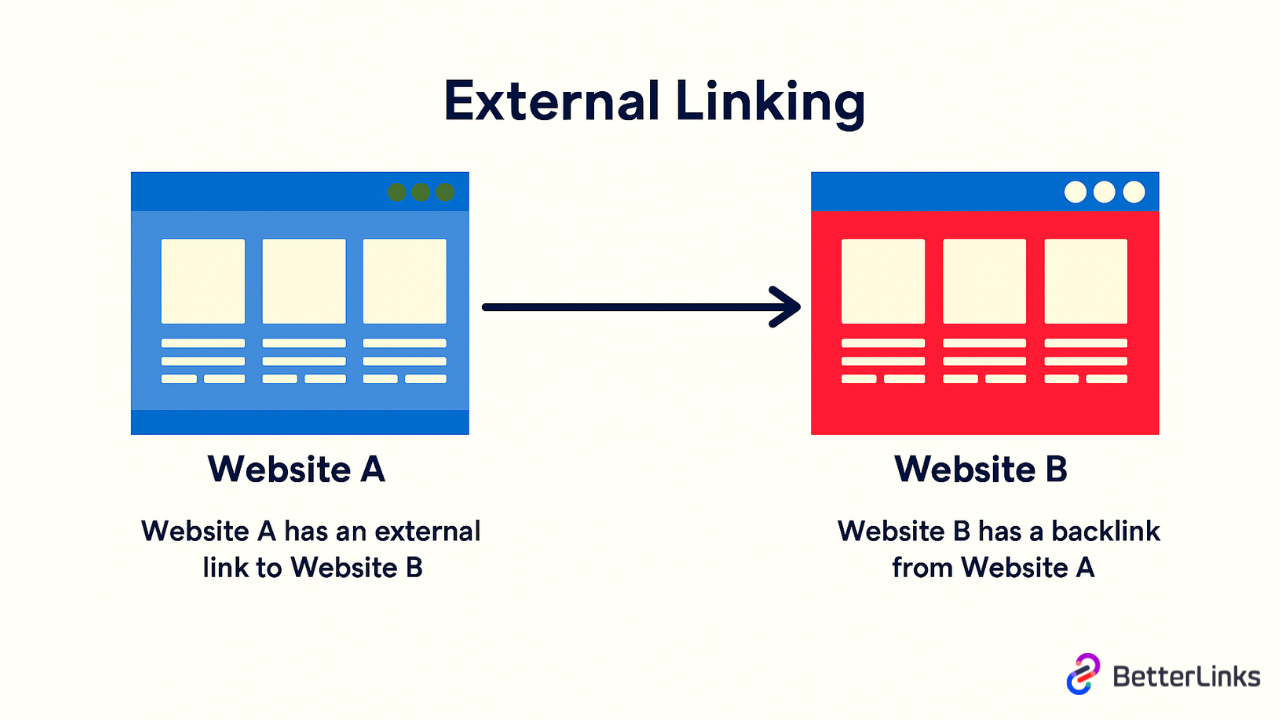
You can think of external links as doorways that lead outside your building. They take visitors to a completely different location. When you link to a news article, a research study, a tool or any website that does not belong to you, that is an external link. These links show that you have done your research and are willing to point your audience toward valuable information regardless of where it lives.
Internal Links vs External Links: Key Differences You Should Know
The main difference between internal links and external links lies in where they point. Internal links keep users on your website while external links send them somewhere else. Here are the primary differences you need to understand:
| Aspect | Internal Links | External Links | Examples |
| Destination and Control | Point to pages within your own website. You have full control over the content, URLs, and updates. | Point to other websites outside your domain. You cannot control changes or removals. | Internal: Linking from a blog post on BetterLinks features to your homepage or another article on BetterLinks. External: Linking to Moz’s guide on SEO best practices. |
| Purpose and Function | Organize site structure, guide visitors, distribute page authority and keep users engaged longer. | Provide references, cite sources, recommend resources and connect to the wider web community. | Internal: Linking from a “WordPress SEO tips” blog to a “Link Building Strategies” blog on your site. External: Linking to HubSpot’s blog for detailed marketing stats. |
| SEO Impact | Helps search engines crawl your site and understand which pages are important. Passes link equity from one page to another. | Signals content credibility and trustworthiness when linking to authoritative sites. Can enhance your content’s perceived value. | Internal: Linking from a category page to a product page to pass authority. External: Linking to Google’s Search Console guide in an SEO blog. |
| User Experience | Improves navigation, helps visitors find related content, encourages exploration and increases time on site. | Offers additional resources, supports content with references but may send users away from your site if not placed carefully. | Internal: Linking from a “How to Use BetterLinks” guide to a “Tracking Clicks” article. External: Linking to an external research report or tool. |
Why Internal And External Links Matter for Your Website
Links are an essential part of any website and understanding the difference between internal and external links is key to improving both SEO and user experience. Internal links connect pages within your own website, while external links point to other websites.
Both play important roles in helping visitors navigate your site, establishing authority and improving search engine rankings.
Internal Links: Guiding Visitors And Boosting SEO
Internal links connect one page of your website to another. They are a cost-free and highly effective way to improve site navigation, distribute authority, and increase user engagement.
🔗 Improved Site Navigation: Internal links create clear pathways for visitors to explore your content. When someone reads a blog post and clicks a relevant link to another article, they can continue their journey smoothly. This reduces bounce rates and keeps visitors engaged longer.

🔗 Better Crawling and Indexing: Search engines use crawlers to discover and understand your web pages. Internal links help crawlers navigate your site more efficiently. Pages that are linked frequently are crawled more often while pages with few or no links may be overlooked or considered less important.
🔗 Link Equity Distribution: Every page has a level of authority, sometimes called link juice. Linking internally allows you to pass this authority from high-value pages to new or important pages, helping them rank better in search results.
🔗 Content Hierarchy: Structured internal links show search engines which pages are most important. Linking from your homepage to category pages and then from categories to individual posts establishes a clear hierarchy and improves SEO understanding of your website structure.
🔗 Increased Engagement: Internal links encourage visitors to explore more pages, boosting page views per session. Higher engagement signals to search engines that your site provides valuable content.
External Links: Building Credibility And Authority
External links point from your website to other authoritative websites. They help validate your content, provide additional resources to readers, and enhance SEO.

🖇️ Builds Credibility: Linking to high-quality sources like Google, HubSpot, or Moz shows readers that your content is trustworthy and well-researched.
🖇️ Improves SEO: External links signal topic relevance to search engines and can support your link-building strategy when authoritative sites link back to you.
🖇️ Enhances User Experience: External links give visitors access to additional information, helping them learn more about the topic and making your content more valuable.
🖇️ Maintains Link Quality: Regularly checking external links for broken or outdated URLs ensures a smooth user experience and prevents negative SEO impact.
10+ Proven Tips for Effective Internal And External Linking
Creating an effective internal linking strategy is simple when you intentionally connect your pages to guide visitors and boost SEO. External links require more care since you are linking to other websites but when used correctly, they enhance content quality and improve SEO performance.
1. Link from High Authority Pages: Your homepage and most popular content pages typically have the most authority. When a strong page passes its link equity to other pages, it helps them perform better.
2. Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. Instead of using generic phrases like ‘click here’ or ‘read more,’ use descriptive anchor text that tells readers what they will find when they click. For example, ‘learn about link building strategies’ is much more informative than ‘click here.’
3. Link to Relevant Content: Only create internal links when they make sense contextually. If you are writing about email marketing, linking to a related article about email list building is helpful. Linking to an unrelated post about web hosting just for the sake of adding links provides no value.
4. Do Not Overdo It: Too many internal links can overwhelm readers and make your content look spammy. There is no perfect number, but a good rule of thumb is to include internal links naturally where they add value. Focus on quality over quantity.
5. Update Old Content with New Links: As you create new content, go back to older articles and add internal links to your new pages where relevant. This helps distribute authority to new content and gives it a better chance of ranking. It also keeps your older content fresh and more useful to readers.
6. Create Content Hubs: Organize related content into topic clusters with a main pillar page that links out to more specific subtopic pages. Those subtopic pages should then link back to the pillar page and to each other where appropriate.
7. Link to Authoritative Sources: Only link to websites that are reputable and trustworthy. Government websites, established educational institutions, well-known industry publications and respected experts all make good external link destinations. Before linking, check that the source is credible and the information is accurate.
9. Verify Links Regularly: External links can break when websites change their structure or remove pages. Regularly check your external links to ensure they still work. Broken links frustrate users and can hurt your SEO.
10. Use External Links to Support Claims: Whenever you make a factual claim, cite a statistic or reference research, link to the source. This practice shows that your information is verifiable and demonstrates intellectual honesty.
11. Open External Links in New Tabs: While this is a debated practice, many sites choose to open external links in new tabs or windows. This keeps your site open in the background so visitors can easily return after checking out the external resource.
12. Be Strategic with Competitor Links: You generally do not want to send traffic to direct competitors without good reason. However, if a competitor has created the definitive resource on a topic and it genuinely helps your readers, linking to it can actually benefit you.
13. Balance Quality and Quantity: You do not need many external links in each piece of content. Even one or two well-placed external links to quality sources can enhance your credibility.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Website Links
Even when you understand the importance of internal and external links, it is easy to make mistakes that undermine their effectiveness. Being aware of these common errors helps you avoid them and maintain a healthy linking strategy.
🔴 Using Too Many Links
Stuffing your content with excessive links makes it hard to read and can look spammy to both users and search engines. Each link should serve a purpose. If you find yourself adding links just to hit a number, you are probably overdoing it.
🔴 Neglecting Link Maintenance
Links break over time as pages move or get deleted. Failing to check and update your links leads to a poor user experience. Broken internal links suggest a poorly maintained site, while broken external links leave readers at dead ends. Regular link audits are essential.
🔴 Using Poor Anchor Text
Generic anchor text like ‘click here,’ ‘this page,’ or ‘read more’ provides no context about the destination. Descriptive anchor text helps users and search engines understand what they will find when they click. Make your anchor text natural and informative.
🔴 Linking to Low Quality Sites
When you link to a questionable external source, you risk your own credibility. Always verify that the sites you link to are reputable, accurate and relevant. Poor-quality external links can actually harm your SEO.
🔴 Ignoring Link Context
Links should fit naturally within your content. Forcing links into sentences where they do not belong or adding links to unrelated content confuses readers. Every link should make sense in context and provide value at that specific point in your content.
🔴 Forgetting About Mobile Users
Many people browse websites on mobile devices where screens are smaller and clicking can be less precise. Make sure your links are easy to tap and that link-rich content remains readable on mobile. Test your pages on different devices to ensure a good experience everywhere.
Bonus: How to Manage Your Links in WordPress?
Managing links across an entire website can become complex as your site grows. Fortunately, several tools can help you create, monitor and optimize both internal and external links more efficiently.
⚙️ BetterLinks for WordPress
If your website runs on WordPress, BetterLinks offers comprehensive link management features. It helps you create and track both internal and external links, monitor click-through rates and organize your links effectively. The analytics features let you see which links perform best so you can refine your strategy.
With BetterLinks, you can also create shortened branded links and manage redirects, all from one dashboard. Key features include 👉🏻
- Link Tracking and Analytics: Monitor click-through rates to identify your best-performing links and optimize your strategy.
- Branded Shortened Links: Create custom short links for marketing campaigns or internal use.
- Redirect Management: Easily manage 301 and 302 redirects to maintain link equity and prevent broken links.
- Internal Link Suggestions: Automatically discover internal linking opportunities to improve SEO.
For more details and clarification, you can check out this blog 👉🏻
Ready to Optimize Your Links?
Internal and external links play different roles, but together they boost SEO and improve user experience. Internal links strengthen your website from within by improving navigation, distributing authority and helping search engines understand your content structure.
External links build credibility, provide additional value and connect your content to the broader internet. Both types matter for your website’s SEO performance and user experience. Is this blog helpful? Join our community to stay updated with the latest blogs, product reviews and WordPress solutions. Subscribe to our blog.




